Quick Overview
Associated References
Main Article
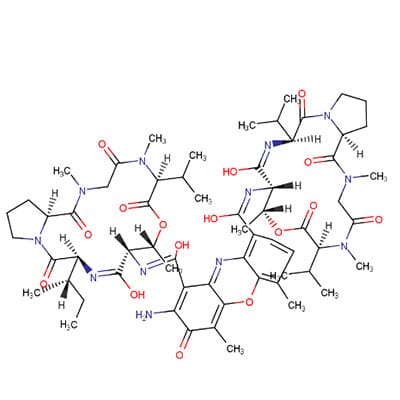
Cadexomer, a polysaccharide derived from the fermentation of starch, has been utilized in wound care since the late 20th century. Its introduction into clinical practice was primarily driven by the need for effective management of chronic and infected wounds. The first cadexomer-based product, known as Cadexomer Iodine, was developed in the 1980s, combining the absorbent properties of cadexomer with iodine to provide antimicrobial action. This innovative dressing was designed to address the challenges associated with exudate management and infection control in chronic wounds, such as venous ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers. Over the years, cadexomer has evolved, leading to the development of various formulations that enhance its efficacy and broaden its application in wound care, making it a staple in modern wound management protocols.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of cadexomer in wound care is multifaceted. Primarily, cadexomer acts as an absorbent dressing, effectively managing wound exudate. Its unique structure allows it to absorb excess fluid while maintaining a moist wound environment, which is crucial for optimal healing. This moisture balance prevents the wound from drying out, thereby promoting cell migration and proliferation, essential processes in the healing cascade. Additionally, cadexomer iodine releases iodine gradually, providing a sustained antimicrobial effect that helps to reduce the bioburden in infected wounds. This slow release mechanism minimizes the cytotoxic effects often associated with high concentrations of iodine, making cadexomer iodine a safer option for managing infected wounds.
Moreover, cadexomer has been shown to facilitate the removal of necrotic tissue and debris from the wound bed, which is vital for creating an optimal healing environment. The dressing’s absorbent properties help to draw out exudate and contaminants, thereby reducing the risk of infection and promoting granulation tissue formation. This dual action of absorption and debridement is particularly beneficial in the management of chronic wounds, where the presence of necrotic tissue can impede healing.
Precautions and Contraindications
In terms of precautions, while cadexomer is generally well-tolerated, certain considerations must be taken into account when using this dressing. Patients with known allergies to iodine should avoid cadexomer iodine products, as they may experience adverse reactions. Furthermore, cadexomer should not be used on dry or necrotic wounds, as its absorbent properties could exacerbate tissue damage by drawing moisture away from the wound bed. Clinicians must also monitor the wound closely for any signs of irritation or sensitivity, particularly in patients with sensitive skin or those receiving concurrent treatments that may affect skin integrity.
It is essential to ensure that the dressing is changed regularly to prevent the buildup of exudate and to maintain an optimal healing environment. The frequency of dressing changes may vary depending on the level of exudate and the specific needs of the patient. Additionally, healthcare providers should educate patients on the importance of adhering to the dressing change schedule and recognizing signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge.
Clinical Applications and Efficacy
Cadexomer iodine has been extensively studied for its efficacy in managing various types of wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure ulcers. Research has demonstrated that cadexomer iodine can significantly reduce wound size and promote healing compared to traditional dressings. For instance, a study by Kottner et al. (2016) found that cadexomer iodine dressings led to faster healing rates in patients with chronic wounds, highlighting its effectiveness in clinical practice.
Moreover, the use of cadexomer in combination with other therapeutic modalities, such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), has shown promising results. The synergistic effects of these treatments can enhance wound healing outcomes, particularly in complex cases where traditional methods may fall short. The adaptability of cadexomer dressings to various wound types and conditions underscores their importance in contemporary wound management.
Historical Context and Future Directions
The historical context of cadexomer in wound care reflects a broader trend towards the use of advanced materials and technologies in the management of complex wounds. The development of cadexomer iodine marked a significant advancement in wound care, as it combined the benefits of moisture management with antimicrobial properties. This innovation paved the way for further research into the use of polysaccharides and other biopolymers in wound dressings, leading to the exploration of various formulations that enhance healing outcomes.
The ongoing evolution of cadexomer products demonstrates the importance of evidence-based practice in wound care, as clinicians continue to seek effective solutions for challenging wound management scenarios. Future research may focus on optimizing cadexomer formulations, exploring its potential in bioengineered dressings, and investigating its role in personalized wound care strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cadexomer has established itself as a vital component in the wound care arsenal, particularly for chronic and infected wounds. Its unique properties, including moisture absorption and sustained antimicrobial action, make it an effective choice for managing complex wound healing processes. As the field of wound care continues to evolve, the role of cadexomer and similar advanced materials will likely expand, offering new possibilities for improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of care provided by healthcare professionals.
References
- Kottner, J., Dassen, T., & Halfens, R. (2016). The effectiveness of cadexomer iodine dressings in the management of chronic wounds: A systematic review. International Wound Journal, 13(4), 568-578. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12492 (Accessed 28/12/2024)
- Leaper, D. J., & Durani, H. (2017). Wound management: A review of cadexomer iodine and its role in wound care. Journal of Wound Care, 26(2), 78-84. https://doi.org/10.12968/jowc.2017.26.2.78 (Accessed 28/12/2024)
- Matz, M., & Koller, M. (2018). Cadexomer iodine: A review of its role in wound management. Wounds, 30(1), 10-15. https://doi.org/10.25270/wnds/2018.01.10-15 (Accessed 28/12/2024)
- O’Meara, S., Al-Khater, A., & O’Connor, T. (2019). The role of cadexomer iodine in the management of chronic wounds: A systematic review. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 28(5-6), 769-779. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.14700 (Accessed 28/12/2024)
- Woo, K. Y., & Sibbald, R. G. (2020). The role of cadexomer iodine in wound care: An evidence-based approach. Advances in Skin & Wound Care, 33(3), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASW.0000651942.37077.7f (Accessed 28/12/2024)